ERCP
ERCP (short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is a procedure in which doctors use an endoscope and X-rays to view injectable dye as it travels through pancreatic and bile ducts and treat accordingly. The doctor identifies the place where the bile duct comes into the intestine and then feeds a guidewire and thin plastic tube into the bile or pancreatic duct and inject contrast agent while X-rays are taken. The contrast agent allows the doctors to see bile ducts and pancreatic duct on the X-rays. Once the problem is identified, then doctor treat it.
Once the source of the problem is identified, the doctor may then treat it by performing one of the following procedures.
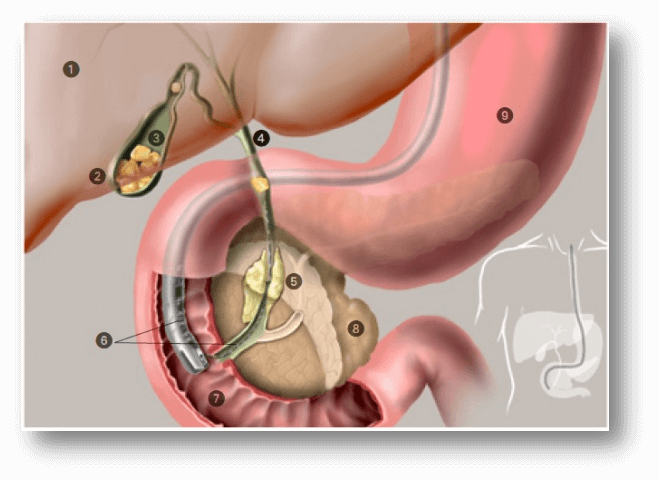
Sphincterotomy
This involves making a small incision (cut) in the opening of the bile duct or pancreatic duct, which can help bile duct stone, bile, and pancreatic juice to drain appropriately
Stent placement.
A stent is plastic or metal tube that is placed in the bile duct or the pancreatic duct to hold the duct open and allow it to drain.
Bile duct or Pancreatic duct removal
ERCP can remove stone from the bile duct or pancreatic duct, but not from the gallbladder itself.
Is An ERCP Safe?
An ERCP is considered a low-risk procedure; however, complications can occur. These can include pancreatitis, infections, bowel perforation, and bleeding. Your doctor will discuss the risks of possible complications before the test.
